Java Evolution Details :
The Java programming Language
Evolved From A Language Named Oak
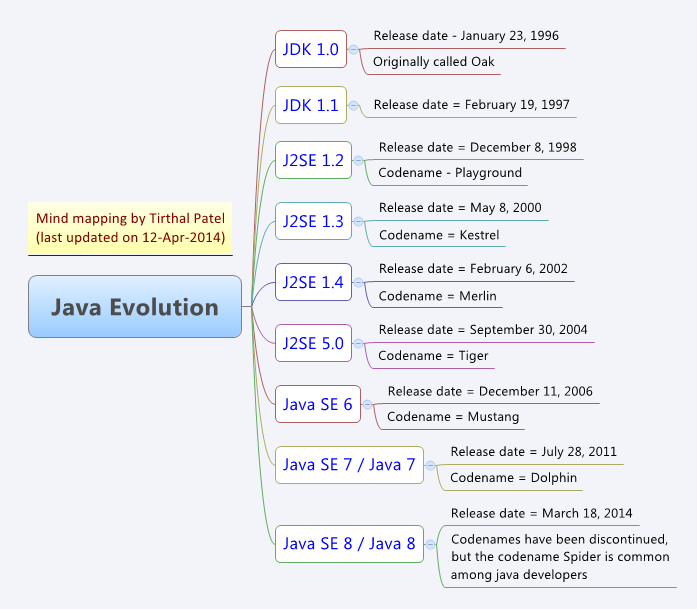
Java was initially launched as Java 1.0 but soon after its initial release, Java 1.1 was launched. Java 1.1 redefined event handling, new library elements were added.
Oak was developed in the early nineties at Sun Microsystems as a platform-independent language aimed at allowing entertainment appliances such as video game consolesand VCRs to communicate .
Just as the deals with the set-top box manufacturers were falling through, the World Wide Web was coming to life.
As Oak’s developers began to re cognize this trend, their focus shifted to the Internet and WebRunner, an Oak-enabled browser, was born.
Oak’s name was changed to Java and WebRunner became the HotJava web browser.
The excitement of the Internet attracted software vendors such that Java development tools from many vendors quickly became available.
That same excitement has provided the impetus for a multitude of software developers to discover Java and its many wonderful features.
Platform Independence - Java compilers do not produce native object code for a particular platform but rather ‘byte code’ instructions for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Making Java code work on a particular platform is then simply a matter of writing a byte code interpreter to simulate a JVM. What this all means is that the same compiled byte code will run unmodified on any platform that supports Java.
Object Orientation - Java is a pure object-oriented language. This means that everything in a Java program is an object and everything is descended from a root object class.
Rich Standard Library - One of Java’s most attractive features is its standard library. The Java environment includes hundreds of classes and methods in six major functional areas.
Applet Interface - In addition to being able to create stand-alone applications, Java developers can create programs that can downloaded from a web page and run on a client browser.
Familiar C++-like Syntax - One of the factors enabling the rapid adoption of Java is the similarity of the Java syntax to that of the popular C++ programming language.
Garbage Collection - Java does not require programmers to explicitly free dynamically allocated memory. This makes Java programs easier to write and less prone to memory errors.
Significant Language Features
- Language Support classes for advanced language features such as strings, arrays, threads, and exception handling.
- Utility classes like a random number generator, date and time functions, and container classes.
- Input/output classes to read and write data of many types to and from a variety of sources.
- Networking classes to allow inter-computer communications over a local network or the Internet.
- Abstract Window Toolkit for creating platform-independent GUI applications.
- Applet is a class that lets you create Java programs that can be downloaded and run on a client browser.
Areas of Application
- World Wide Web Applets
- Cross-Platform Application Development
- Other Network Applications
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon